Trade facilitation is a newly established focus area at the Coega Special Economic Zone (SEZ), located in the City of Gqeberha, Nelson Mandela Bay Municipality, South Africa. The focus area brings together customs, investor services, and logistics to the internationally acclaimed and award-winning 9003ha Coega SEZ and Nelson Mandela Bay Logistics Park (NMBLP), says Graham Taylor, CDC’s trade facilitation manager.
Emerging perspectives indicate that growth reforms in the SEZs and seaports complex need to be pursued in five thematic areas, namely: modernising transportation networks; enhancing competition; labour-intensive growth; trade policy; and export competitiveness and regional growth opportunities. While there is an assumption that seaports bring local economic development, advances in transportation technology indicate the need for logistics industries to support these ports.
Trade facilitation measures are particularly beneficial to developing countries, which generally take three times as many days to export goods, with twice as many documents, and six times more signatures than developed countries. Trade facilitation can be defined as:
The simplification, standardisation and harmonisation of procedures and associated information flows required to move goods from seller to buyer and to make payment.
The CDC operates on the principle that trade facilitation measures are not the preserve of a single government department or entity, and collaboration is often a necessity. The CDC’s trade facilitation will give effect to the Trade Facilitation Agreement which South Africa ratified in 2017, and the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) which commenced in 2021.
The CDC addresses the challenge of facilitating trade through focusing on areas such as: customs, environmental compliance, infrastructural services, investor services, logistics, security, and spatial planning. Whilst considerable progress has been made, thereby establishing the CDC as a best-practice leader in all these areas, considerable scope exists for harmonisation, simplification, standardisation, and transparency of procedures which are increasingly becoming complex.
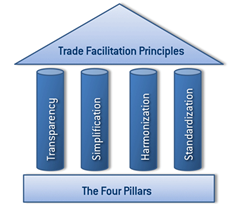
The principles of trade facilitation are identified in the graphic hereunder, as identified from the UNECE (2012) Trade Facilitation Implementation Guide.
Figure 1 - The Pillars of Trade Facilitation
A key area is the somewhat ubiquitous One-Stop-Shop, a concept widely established through intent, yet infrequently applied in meaningful ways for trade facilitation. To give effect to the One-Stop-Shop, as a mechanism to support trade facilitation, the CDC has developed practical interventions which directly assist investors in the Coega SEZ, as depicted below.

a) One stop to locating in the Coega SEZ
Investment decisions are notoriously complex, and the CDC has removed many of the obstacles to investment by establishing a planning and development framework which enables a plug and play environment. Land has been appropriately rezoned into a development framework which supports maximum flexibility. Potential environmental impediments are pre-identified and liaison forums are established for easing environmental authorisations should such be required. The process for obtaining local authority approvals for the construction and operations of business within the SEZ has been significantly shortened. Investors are also being provided with services timeously and according to their needs.
b) Incentives
Incentives have often been cited as a major determinant for investment decisions. The CDC’s approach to trade facilitation has focused on ensuring timeous access to available incentives using the trade facilitation principles. In so doing, investment decisions have been expedited and investors have benefited from the full package of incentives from all spheres of government.
c) Customs
Customs is often at the core of many trade facilitation interventions, and in the Coega SEZ it is no different. Customs Controlled Areas (CCAs) have been established. The process of establishing CCA Enterprises is now well established and administrative delays have been eliminated. In addition, the Coega SEZ now offers customs-controlled warehouses dedicated to activities such as the packing and repacking of bonded cargo.
d) Investor Services
Through the One-Stop-Shop, the CDC offers electronically based and ISO-certified systems and processes which ease the process of operating a business within the Coega SEZ. Any constraints faced by investors are quickly and efficiently dealt with and regular interactions between investors are supported to enable the development of the agglomerative economies which are at the core of any successful SEZ.
e) Labour Framework
Labour underpins successful trade facilitation, and the CDC provides an enabling environment for sound labour relations through a social compact amongst all role-players in the form of a Zone Labour Agreement (ZLA). In addition, through its Human Capital Solutions (HCS) interface, Coega offers services such as medicals, inductions of new employees, skills training, and access to labour that is registered on the web portal, i.e., Coega’s Gateway to Opportunity (G2O) database.
The operating environment of the Coega SEZ has provided an ideal platform for introducing a range of practical interventions aimed at facilitating trade. The interventions are undoubtedly a key factor for competitive advantage for the Coega SEZ - a preferred investment destination and leading SEZ in Africa. Therefore, the role of trade facilitation is central to ensuring a transparent, simplified, harmonised and standardised operating environment, concludes Taylor.
For more information, contact Gerda Smit on: 041 403 0564 or Gerda.Smit@coega.co.za